Rheumatoid arthritis, commonly abbreviated as RA, is an autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation. While RA primarily affects joints, inflammatory responses may also occur in the skin, heart, lungs, and other organs. Though some hypotheses exist, there is currently no known single cause for RA. Gout is a form of (usually) acute arthritis that has a known cause, namely the buildup crystalline uric acid deposits in the blood and joints. These crystals cause an inflammatory response, often in a big toe.
RA and gout can be very painful disorders, but gout tends to be more treatable and has a better prognosis in most cases. To diagnose the presence of either RA or gout, a physician must perform a series of diagnostic imaging tests. To differentiate between gout and pseudogout, fluid may also be drawn from inflamed joints for testing.
Comparison chart
| | Gout | Rheumatoid Arthritis |
|---|---|---|
| Joint Symptoms | Arthritic joint pain, swelling, redness, warmth, and extreme tenderness. In some cases, the development of tophi | Joints are painful, swollen, and stiff; affects joints symmetrically; affects smaller joints such as hands & ankles. Systemic with exacerbations and remissions |
| Treatment | Resting the joint and applying ice, NSAIDS, corticosteroids, colchicine (a painkiller), medications that target uric acid production or excretion, healthy diet low in purines (from alcohol, meat, fish). | NSAIDs, steroids (prednisone), DMARDs (Methotrexate), antimalarial (Plaquenil), corticosteriods |
| Diagnosis | Imaging tests, drawing fluid from the swollen joint for analysis, blood tests | 1- Anemia (ferratin, ion. ion binding capacity) 2- bone (inc ALP) 3- Inflammatory markers (C reactive protein and ESR) |
| Presence of symptoms affecting the whole body (systemic) | Chills and a mild fever along with a general feeling of malaise may also accompany the severe pain and inflammation | Dull pain and inflammation Frequent fatigue (afternoon), stiffness, ulnar deviation, muscle atrophy, swelling of the knuckles , synovial Thickness complications: joint fail, depression, Osteoporosis, infections surgical complications |
| Cause | Hyperuricemia — overabundance of crystalline monosodium urate (uric acid) deposits in the blood and joint fluid. | Classified as an autoimmune disease, No real known cause.-Connection between environmental and genetic factors;female reproductive hormones |
| Associated symptoms | Tophi may form.These are large masses of uric acid crystals, which gets collected in the joints and damage it.They also gets collected in the bone and cartilage, such as in the ears. | Frequent feelings of "being sick inside," with fevers, weight loss, or involvement of other organ systems. carpal tunnel Extra-articular manifestations: nodules, vasculitis, pulmonary, cardiac, skin (vasculitis), eye (sjorgen's syndrome, scleritis |
| Disease Process | metabolic desease | chronic Autoimmune |
| Gender | More common in men than women; in women after menopause | Affects more women than men |
| Pattern of joints that are affected | Joint of the big toe most commonly affected. other joints affected are of ankle, heel, knee, wrist, fingers, elbow etc. | Symmetrical - often affects small and large joints on both sides of the body, such as both hands, both wrists or elbows, or the balls of both feet |
| Age of onset | usually over 35 yrs of age in men and after menopause in females | 35-45 years old |
| Speed of onset | sudden onset | Rapid, within a year |
Cause
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a disease in which your own immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue, causing inflammation that damages your joints.
On the other hand, gout results from deposits of needle-like crystals of uric acid in connective tissue, joint spaces, or both. These deposits lead to inflammatory arthritis, causing swelling, redness, heat, pain, and stiffness in the joints. Gout accounts for about 5% of all cases of arthritis.
Signs and symptoms
- RA usually causes pain or stiffness lasting for more than 30 minutes in the morning or after long rest and lack of activity. Stiffness due to gout is present only at the time of the attack.
- RA is associated with symmetrical swelling e.g., both hands, both elbows, etc. whereas Gout either involves a single joint or involves the joints in an asymmetric pattern.
- Most typically, RA symptoms include joint pain, swelling, tenderness, and redness of the joints; prolonged morning stiffness; and less range of movement. Some people also experience fever, weight loss, fatigue, and/or anemia .On the other hand the patient having Gout suddenly experiences a hot, red, swollen joint, caused by the formation of uric acid crystals between the joints. The attack often occurs at night and in a single joint, with the pain becoming more severe. Chills and a mild fever along with a general feeling of malaise may also accompany the severe pain and inflammation.
- In Gout although the pain and swelling disappear with treatment, it almost always returns in the same joint or in another one. Whereas RA is a continuous and progressive disease with no remissions.
Location of joints involved
With RA, inflammation generally occurs in the knuckles and at the joints closest to your hands, nearer the base of your fingers. On the other hand, gout usually affects the joints in the big toe.Some other parts that could get affected by gout are ankle, heel, knee, wrist, fingers, elbow etc.
Prevalence
Adult men, particularly those between the ages of 40 and 50, are more likely to develop gout than women, who rarely develop the disorder before menopause. People who have had an organ transplant are more susceptible to gout. On the other hand, RA is much more common in women.
References
- Harrison's principals of Internal medicine volume 1 15th edition
- Current Medical Diagnosis and treatment, 2004; Lange publications.
- About.com article
- iVillage.com article on RA
- iVillate article on Gout
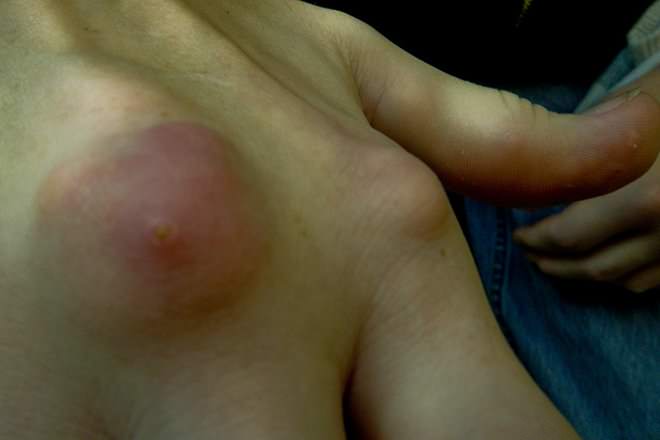

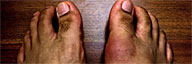 Gout
Gout 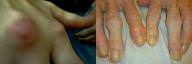 Gout
Gout  Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis  Type I
Type I  Back Pain
Back Pain  Cancer
Cancer
Comments: Gout vs Rheumatoid Arthritis
Anonymous comments (4)