Components of an electrical circuit or electronic circuit can be connected in many different ways. The two simplest of these are called series and parallel and occur frequently. Components connected in series are connected along a single path, so the same current flows through all of the components. Components connected in parallel are connected along multiple paths, so the same voltage is applied to each component.
A circuit composed solely of components connected in series is known as a series circuit; likewise, one connected completely in parallel is known as a parallel circuit.
Comparison chart
Understanding Series and Parallel Circuits
In a series circuit, the current through each of the components is the same, and the voltage across the circuit is the sum of the voltages across each component. In a parallel circuit, the voltage across each of the components is the same, and the total current is the sum of the currents through each component.
The YouTube video below offers a good explanation of series and parallel circuits, and how the arrangement affects the amount of current flowing through the circuits in accordance with Ohm's Law (even though the thumbnail gives the impression that the video may be broken, it still works):
Resistance, Inductance and Capacitance in Series vs. Parallel Circuits
Voltage
In a series circuit the voltage is addition of all the voltage elements.
- V = V1 + V2 + ... + Vn
In a parallel circuit the voltage is the same for all elements.
- V = V1 = V2 = ... = Vn
Current
In a series circuit, the current is the same for all of the elements.
In a parallel circuit, the current in each individual resistor is calculated via Ohm's law.
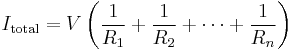 .
.
Resistors
Resistance and conductance in series circuits
Total resistance in a series circuit is simply the sum of the resistances of individual resistors.
Conductance is the inverse of resistance. So total conductance of a series circuit is calculated via this equation:
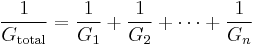 .
.
Resistance and conductance in parallel circuits
Total resistance in a parallel circuit is calculated like conductance in a series circuit:
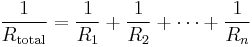 .
.
Conductance in a parallel circuit is simply the sum of conductance for individual elements:n:
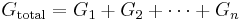 .
.
Switches
Two or more switches in series make a logical AND operation. The circuit carries current only if all switches are closed (On). But in a parallel circuit, two or more switches make a logical OR gate. Current flows as long as any one of the switches is closed.



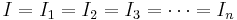
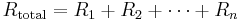
 Current
Current  AC
AC  Electric Field
Electric Field  Energy
Energy  Speed
Speed  Heat
Heat
Comments: Parallel Circuit vs Series Circuit